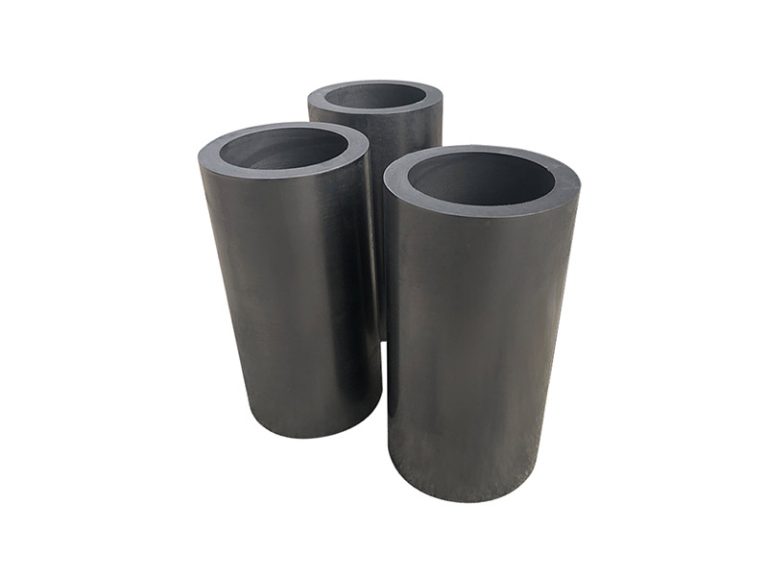
Graphite is often used as a lubricant in the mechanical industry
Graphite is widely used in piston rings, seals and bearings for the transportation of corrosive media. No lubricant is required for operation. Graphite emulsions are also good lubricants for many metal processes (wire and tube drawing).
Graphite in the mechanical industry manufacturing applications
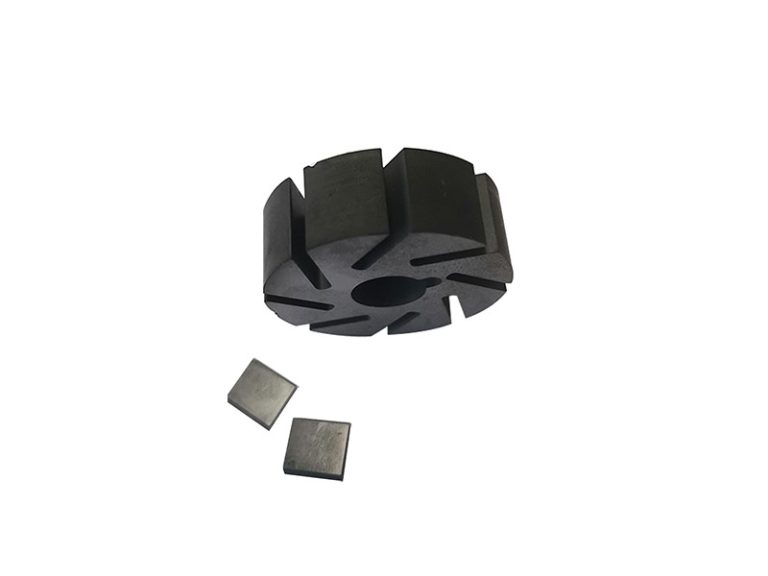
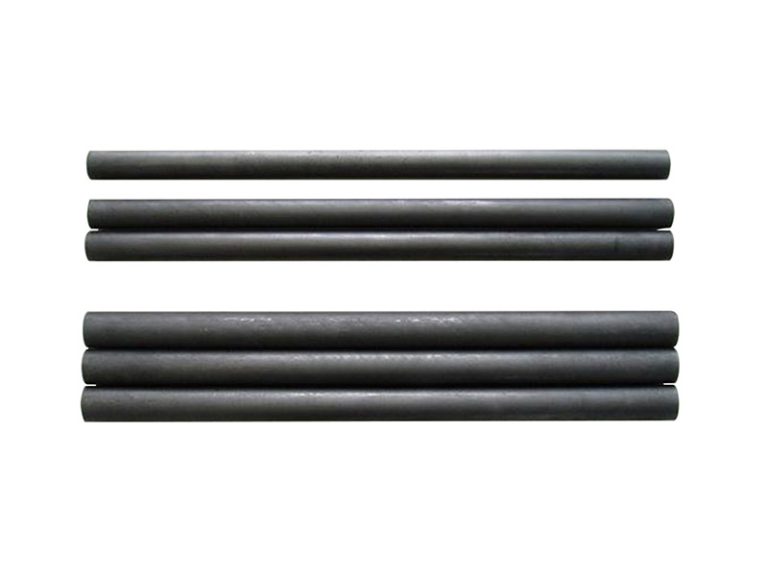
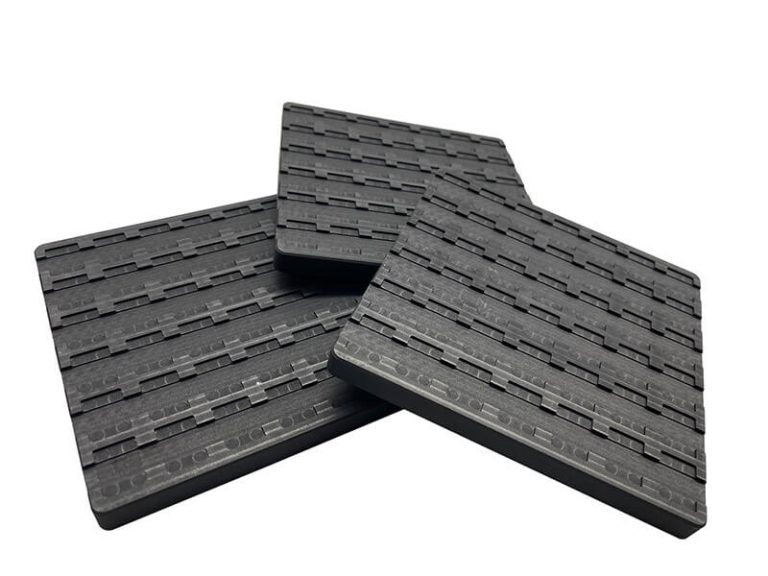
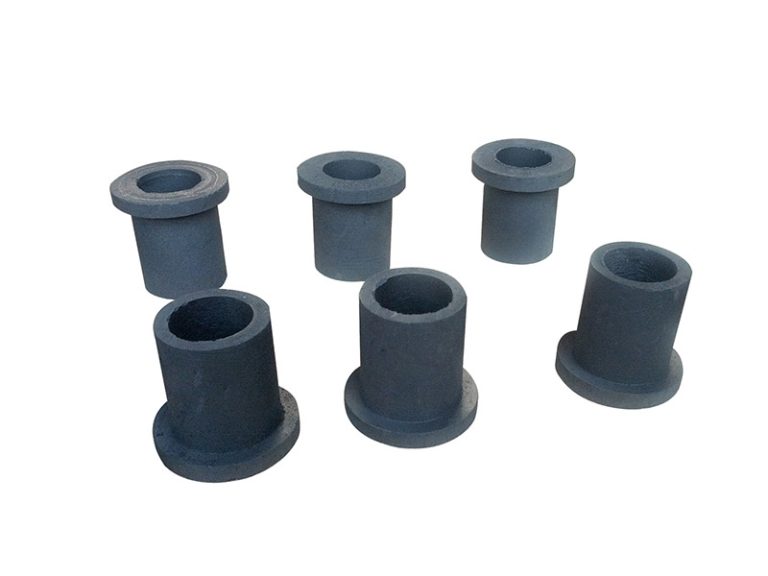
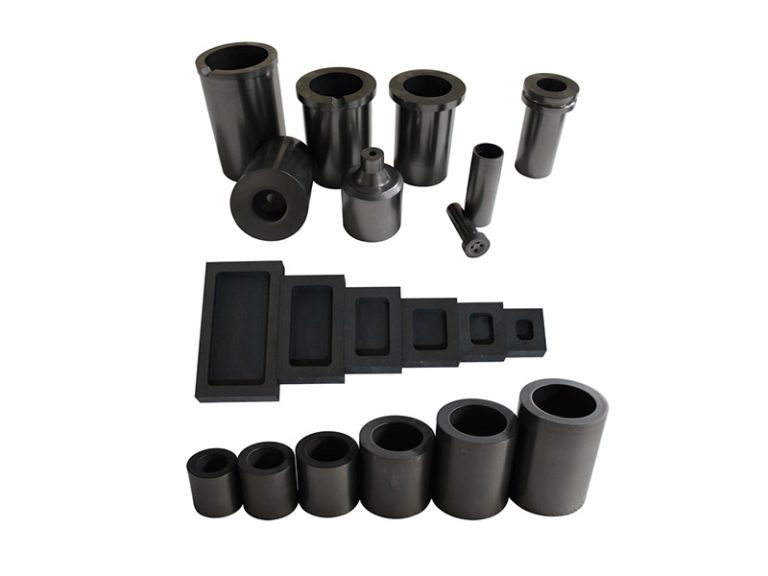
Graphite bearings, thrust bearings, graphite rotors, guide ring impellers, wear control friction parts, dynamically sealed rotary plugs and piston rods.
Graphite bearings are used in places where normal bearings cannot be used due to high temperatures. For example, graphite bearings can be used to ensure the normal operation of high-temperature feeders, flame tube gas vent doors and blowers in boiler preheaters, flue valve regulators, and charging machines in the steel industry.
Graphite is widely used in aerospace field because of its self-lubricating properties, easy molding and processing, good thermal conductivity, thermal stability and chemical stability, such as sealing materials, throat lining materials, brush materials, aerospace equipment parts, insulation materials and radiation resistant materials, such as graphite rings for aviation, piston rings, aviation bearings, graphite sealing parts for aerospace.
In the military industry, isostatic graphite can be used to manufacture graphite nozzles for solid fuel rockets due to its small expansion coefficient, and the non-magnetic properties of graphite can be used as nose cones for ballistic missiles. It can be used as throat lining material for small rocket solid rocket motors. Graphite's electrical conductivity and abrasion resistance are used as brush materials for various engines, inverters and motors.